Assessment of Auxetic Structures Under Impact Loading
Lattice structures have been used in energy absorption systems for many years. Honeycomb geometry is a common choice for the lattice core of these structures, but more recently, auxetic geometries have been introduced with a unique feature, the negative Poisson's ratio, which can be used in some structures instead of honeycomb. Having negative Poisson's ratio causes these structures to have different mechanical properties than ordinary structures; one of these features is high energy absorption which has been studied in this study.
In this study, the energy absorption properties of three different types of auxetic structures under quasi-static and low velocity impact loadings have been investigated. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) was used to fabricate the specimens, and the auxetic structures with geometries including re-entrant, arrowhead and antitetra chiral geometries were compared with conventional non-auxetic honeycomb structure, in terms of compressive strength, energy absorption, and other mechanical properties.
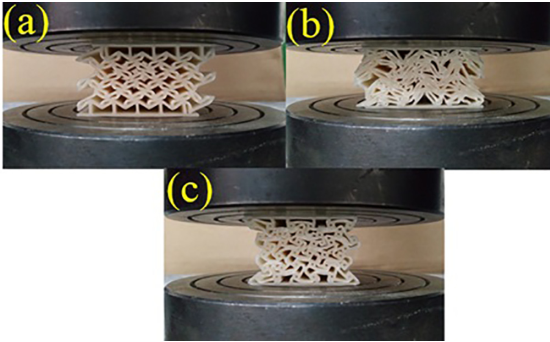
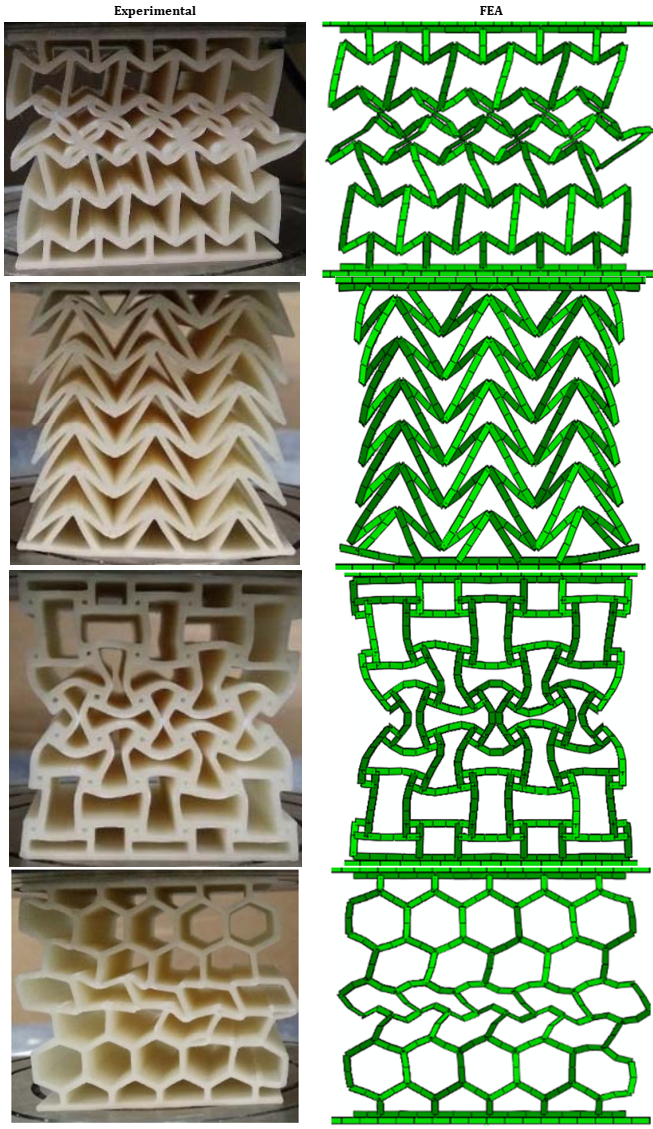
It was found that the auxetic structures had better mechanical properties in both types of loading and the antitetrachiral structure showed the best performance overall. In addition, it was concluded that there was no correlation between the performance of some structures such as arrowhead in low velocity impact loading and quasi-static loading. Moreover, numerical simulations with finite element method (FEM) were done to compare with experimental results and to study the collapse and deformation patterns of the structures that a good approximation between the experimental and numerical results was observed. Finally, using validated numerical model, a parametric study was performed on the anti-tetra chiral structure as the best structure. Parametric study showed that maintaining the overall dimensions of the structure, changing the size and cell number of unit cells did not significantly affect the performance of the structure. Also, the optimal ratio between the numbers of unit cells in transverse to longitudinal directions was obtained. Moreover, a modified structure was designed and introduced and its properties was studied and compared with other structures.
Selected Journal Papers
- Najafi, Milad, Hamed Ahmadi, and G. H. Liaghat. "Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Energy Absorption in Auxetic Structures under Quasi-static Loading." Modares Mechanical Engineering 20, no. 2 (2020).
- Najafi, Milad, Hamed Ahmadi, and Gholamhossein Liaghat. "Experimental investigation on energy absorption of auxetic structures." Materials Today: Proceedings 34 (2021): 350-355.
